Operation: House of Cards
January 4, 2019
The DarkSide of D3fC0n
January 5, 2019Article from June 2017
The power of Awareness through Risk Intelligence and Recon is still widely unrecognized…
We have had some pretty interesting discussions this week and also have some new customers that we will talk about at some later time. While on the road, many folks who do not do Intelligence or have been trained in such understand sometimes just how valuable Risk Intelligence is. Discussions with new partners, customers and other researchers starting out are a great way for me to explain the “magic” and theory behind our Risk Intelligence Reports and Solution Suite NeedleStack/CyberNsight.
Risk intelligence and using its information is a huge advantage when you are looking for new potential threats. There are many recent events that may have been identified had people used risk intelligence to find signs of potential threats being exploited. This is by no means a fully automated process but doable and pending the right amount of openness in solutions and a kick-start program that we have to get you going at looking in the right places to get a start.
Two examples that I would expand on are:
- Finding activities that are questionable at best and down right suspicious at worst
- Finding new attack tools, vectors and groups planning something against you
Use Case 1. We have a lot of people that want privacy in the Darkweb. Most of those people are law abiding and actually really nice and cool. Sometimes as in every case of technology though, you have those idiots and jerks that use anonymity to hide more darker activities that can and do result in some of the attacks we found just recently. One of the many reasons my people can’t find these groups or threats is simply because they have constraints in a few areas that when addressed could help immensely.
- Trained People that can pick up unstructured and structured data
- Scoring results of hits based on probabilities that they are relevant
- Using returned results in any tool or solution to followup on potential leads of a group or suspicious activities
To get things started we would use an initial search to find starting points (either in the open network or darknet services pages).
After starting the initial search, we can choose the appropriate searching options we want that will return results, always having the option of tweaking and modifying those results as the searches become more clear or granular. While all this is going on we save results for protocols and also future reference. Why? Well just in case we missed something before we can go back to previous results and review them for new evidence.

The result above is for any relevant clues in normal internet websites that we can get to use for a dedicated search of people looking at these websites, seeking information from them and then also who offers this information. Depending on the hits some are more relevant than others. Here we see a weakness and strength of Bayesian Probabilities as we are collecting data based on indicators or markers that we will then use in a second more detailed search to get better results much faster than with any other method so far. Some caveats to remember are that Bayesian Probabilities are generally up to a max of 80% accuracy (at best) so we want to make our chances of getting better hits by creating a platform that learns from each returned hit (Neural Networks concept). Over time as we search sites we develop a sense for what is returned as relevant for certain catagories and what isn’t. With search parameters that are flexible we can side track all the marketing sites that are actually worthless to our specific search and then start to invest our time more wisely on hits that are more relevant to us and the mission we have or our goal of higher security in tangible ways. The aspect of being open guarantees that the search is not locked down by someone’s version of what is or isn’t relevant but rather a consensus of what is likely to be correct. In that we cluster things into logical groups we increase the potentiality that relevant data is returned quickly. Much of our IP has gone into creating a way to tap probabilities while still being neutral and fully customizable.

After going through initial results we then get to more details that have probabilistic scoring that rapidly increases the likelihood that we are looking at something relevant. In this case we can see that 3 clusters have returned results that are pre-scored and then can help us speed up analysis by up to 90%. This speed up due to neutral, flexible and self learning mechanisms and our technology can help you concentrate your time on what really is relevant. This relevancy can be configured to your business, country, risk profile, etc. so that we eliminate the emotional and individuals perspective. We have pre-defined rules, searches and options to get you going even though you may have never done these kinds of searches. We also provide these reports and services for you so that all you have to do is give us an email so that alerts and research reports that our teams do, get sent directly to you.
Use Case 2 Finding interesting tools that can be used to break into your networks or business.
We reporting about how information that is released also leads to new attacks and the reason for this is simple. When for instance Shadow Brokers (China/Russia???) or Wikileaks (Russia, Assange, ???) releases new code samples for “auction” or selling then we also see that any and all code that is released is grabbed immediately for consumption by different groups, some of those groups are actual crackers and others nation-states (this is where it gets really scary and causes massive disruptions in critical infrastructure). As these groups mix attacks together it becomes almost impossible to actually identify who is doing what. In this specific case Risk Intelligence adds so much more value than a point solution like Firewalls, SIEM, AV etc. Don’t get me wrong, they all have their places but they also all need Risk Intelligence to become aware (situational awareness) of what is really going on.

Many groups monitor Wikileaks and ShadowBrokers for new releases. As these releases are made public through both “normal net” and “darknet” channels we then see uploads that are obviously downloaded, scanned and then reverse-engineered to understand what the code actually does. What increases the spread of these leaks are reposts after data is taken down so that multiple actors and testers can still get to the executables long after the data has been taken off the “normal net”.

Once the information or data becomes available we start to see the first scans and attacks that leverage this new data, the use of these “new” vectors as well as the choice of targets are what are more interesting in many cases. One of the issues here is timing and who starts first (as well as why). When we look at sensors we start to see these attacks happen either before the dump or just after it or both. What we like to know is who started when and with what. This is an indicator of who “might” be behind the leaks, breaches and data being released to the public.
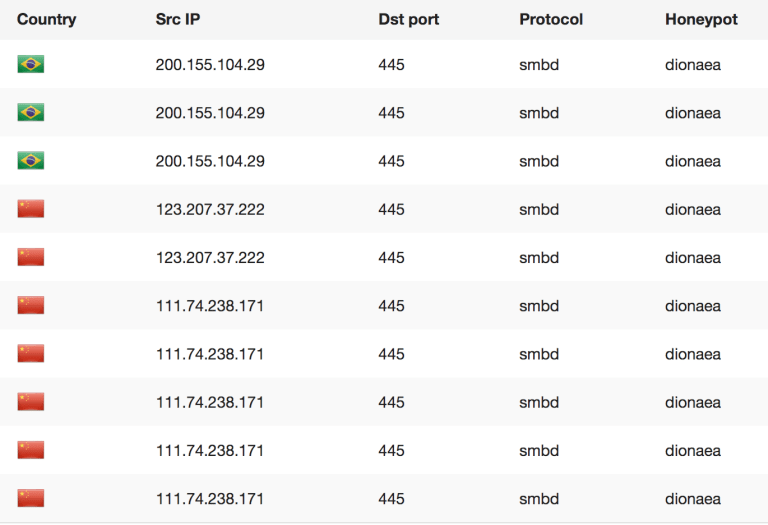
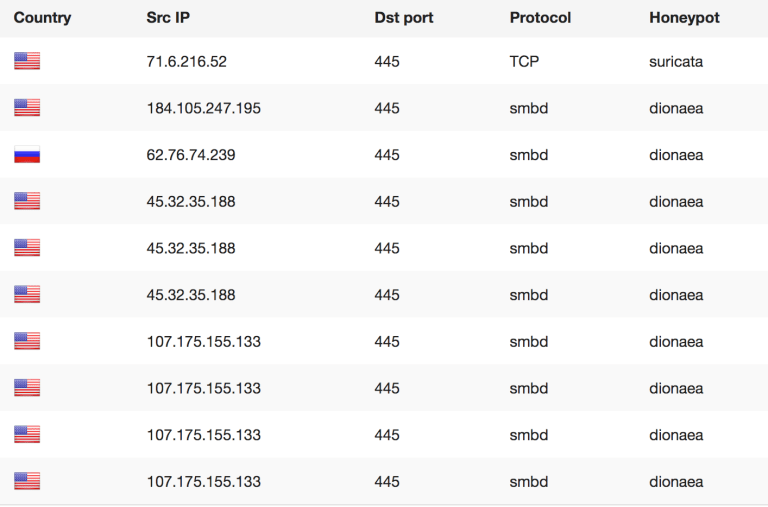
Relying on who the first attacker is, doesn’t always make sense as we need to see the context of this attack and look at the possible bigger pictures here. For instance Wannacry was said to have been from North Korea, even though there was no IP or Attacker based evidence of this. Why this is dangerous is because code is constantly being reused by multiple groups that get new ideas from leaks such as ShadowBrokers and Wikileaks. Once code is released and spread out, you can no longer say who will use it for what and when. Taking original code as a signature or indication of who the attackers are is shortsighted (at best) and completely wrong in our current malware market mentality on the darknet. Currently we already reported about how cheap malware code is in some cases (2$) and that these samples are traded amongst groups to develop them further. The fact that there is money to be made creating new malicious code is one of the foundational problems that AV can never resolve. Its basically a cat and mouse game were the likelihood of getting caught is low, easy money is high and you have a high demand mostly from actors that sell cyber weapons and also services to Nation-States as proxies to keep “plausible deniability”. What this type of “hype” news does is lead people down a rabbit hole that is false, costly and very dangerous as you tend to focus on the wrong things and are lead into a “false” sense of security when reality is completely different. If we focus on the wrong idea then the data we collect will only serve to prove that point (we are right about being wrong). Risk Intelligence however lives from neutrality and collecting evidence about POSSIBLE threats so we can not assume anything otherwise we focus on one small aspect of something potentially much, much bigger. So in this case when I only have 10 minutes to search for something, how can I use that time to get the best and maximum result for my money and invested time. Is looking at existing attacks going on really helping me or is being aware of what can happen so I can prepare for a potential attack better?
If we take the SMB and network aspects of Vault7 (Wikileaks) and ShadowBrokers (China/Russia – assumption) we then take this new released information to check out what the risks to Cisco routers, etc really was, is and will be. So using the same search lets look at cisco hacking searches:

The results above show us some relevant hits that talk about hacking cisco routers and some of these websites are older (so not really caused by shadow brokers but they were looked at after new data was released by shadowbrokers and wikileaks). So the very fact that these two groups releases information (wether true or not) results in an increase of attacks on old and sometimes newer threats to networks and infrastructure. The question then becomes who is the bigger risk, the possible breaches of secrets and security breaches these groups (found) which in some cases from our research where not actually new. We see both groups as high risks that need to be tracked, not because the information (or their version of a truth) but merely the fact that they caused an increase in cyber war, espionage and crime as a direct result of their leaks.
So now in this context lets check out two interesting tools that you can use very easily to breach WiFi routers and permitter defenses of any company. These tools are RouterScan and dSploit(apk).
As data came out to Vault7 and Shadowbrokers we did searches to determine what new risks were going to happen as a result of those breaches. Based on sensor data and historical attack data we first looked at what breaches and leaks happened before both the groups released their information. We found some interesting results that indicated a more advanced campaign that targeted some pretty big names in the industry.
The search I started with was “stealing cisco router configuration” just to see what was out there. The query came back with quite a few older and some newer results. One result was for a Russian Cracker group that listed an older tool by Staas’M called Router Scan.

Router Scan is actually so simple you don’t really need to know that much about networking to use it. You just need to have some basic knowledge of how WiFi works, what IP groups may be interesting, a laptop with windows or Linux and some time as well as a WiFi connection to pull information in from. This also applies to DroidSploit with the difference that DroidSploit only requires a slightly newer Android based smartphone to use.

In the picture above we see that a simple program that has a new input areas needs to be filled up with additional information to be more successful. What you can however also do with this tool is use different exploits, passwords and technology detection to find other WiFi based devices on a nearby network. This is a bit simpler than using Arp tools from Metasploit. Lets take a closer look at what components we have in this nice little software tool that can help you get up to speed on what the risk profile really is.
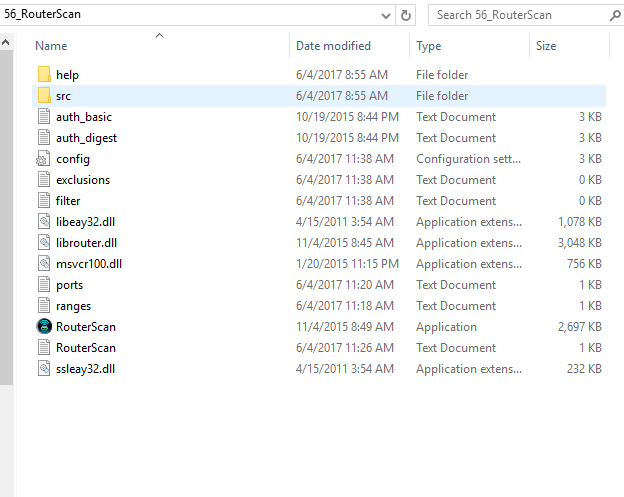
In the directory above for RouterScan we see a few folders and files, lets go through this briefly and explain what they mean in the context of scanning your permitter routers in general and your WiFi routers specifically.
The folders auth_basic and auth_digest contain pre-populated user and passwords that you can use to attempt a login on any router and user dump enough or not knowledgeable enough to change standard passwords in routers. This in itself is by no means just limited to WiFi and Chinese Routers but also the bog guns like WatchGuard, (insert company here), and Cisco. Folks need to understand that initial configurations need to have complex passwords or certificate / key based logon if they need ssh enabled.
The ports folder contains the ports you are scanning for. I changed my configuration to also look for 443, 445, 21 and 22 respectively. Standard ports like 80, 8080 are already pre-populated and ready to go for you. Adding additional ports absolutely makes sense since you may find many surprised hits for printers and other web-based devices that have ports open that you did not enable.
Lastly the ranges folder simply contains those IP ranges like 192.168.0.0/24 etc that you will use to test available routers are responding. You can easily modify this to look for other ranges which increase the attack surface. Some interesting hits you will get are any house automation devices, these devices are very easily pwnd (owned) by attackers if they have busybox linux with hardcoded passwords and a lack of security options. This is a quick tool that you can use to test these devices out and dramatically improve your security as a result.
dSploit the Android Mini-Metasploit.
dSploit is an interest .apk file that you can use to install metasploit like options on an Android phone. Its pretty useful if you can get non-infected APK files which is becoming more and more difficult.

As with RouterScan you have multiple options that enable you to check the security options on a WiFi network you are currently connected to. I find this tool especially useful to show people how easy it is to sniff traffic on an open WiFi network. What makes this tool really useful is the fact that it will already show you routers who’s key algorithms are so weak that they can be easily cracked (Routerpwn). I talked about this issue on PowerLine devices previously so I encourage you to revisit that post on this website.
- The Trace option does a trace route on the router you are interested in
- Port Scanner is obvious, it scans open ports and lists the results
- Inspector checks OS and services detection using deeper scanning
- Vulnerability Finder checks the NVD for vulnerabilities for the indentured OS and services on the router
- Login Cracker offers multiple “services” you can use to attempt to crack network logons
- MitM as it says uses man-in-the-middle attack techniques to get information and help you breach aspects of the network. It also helps you to sniff traffic (simple and password sniff) to pick out passwords and logins to various services of people using the WiFi without any encryption (VPN).
- Session Hijacker is used to listen for cookies and use these to hijack connections
- Kill Connections Kill connections preventing the target to reach any website or server
- Redirect Allows you to redirect all the http traffic to another address
- Replace Images Allows you to replace all images on webpages with the specified one
- Replace Videos Allows you to replace all YouTube videos on webpages with the specified one
- Script Injection enables you to Inject a JavaScript in every visited webpage of victim
- Custom Filter Replace custom text on webpages with the specified one
This toolset by the way also lists some of the most dangerous types of attacks that nation states have done in the past with customized tools and solutions. These types of solutions were used to connect to last mile DSL and other connects and used injection features that you see listed here to infect your PC. Interestingly some of these redirect features are also seen in the latest Fireball attacks that are said to originate form Rafotech a “marketing” company associated with China’s Espionage Agency (APT-RedDragon). But this is data for another post soon
If you enjoyed this please repost and mention us, if you want to avoid many of these “toys” take advantage of our service, you will join a great customer base that we are happy and honored to work with. We also have a lot of fun with our customers.
Until then, stay safe, focused and have fun!
M